fpvectorial - Text Document Support
fpvectorial - Text Document Support
About
The fpvectorial library can be used to create formatted text files in a variety of file formats. Current file support includes Open Document XML (odt) and Open Office XML (docx). The files can be opened in a variety of products including Microsoft Office, OpenOffice and LibreOffice.
As the name suggests, the FPVectorial library was originally created solely as a vector based image library. Support for creating documents was added to FPVectorial as the existing architecture already had the concept of a Document containing Pages, and it's architecture was easily extendable. Document support was added beside the existing image handling classes. Vector based images are differentiated from office documents by the type of page added to TvVectorialDocument.
At this time, two different pages can be added to TvVectorialDocument:
- TvTextPageSequence: This is used by all Office Document writers.
- TvVectorialPage: This is used for Vector Image writers, and is currently ignored by the office document writers.
Currently there are two Office Document writers.
- TODTVectorialWriter.pas: for producing .odt files suitable for opening in OpenOffice and LibreOffice
- TDOCXVectorialWriter: for opening files in Microsoft Office 2007 onwards.
Instead of focusing on the requirements of each individual file format, Office Document support inside FPVectorial was added by creating and implementing a Document Class Hierarchy. It is then up to each individual reader and writer to interpret this class hierarchy.
Alternative Library - fpOdf
If you want to produce an ODT file by concentrating on the File Format, then the fpOdf library implemented by dgaspary and made available on the forums is recommended. This allows fine control when creating an ODT file, including many options not provided by FPVectorial - Document Support. A deeper understanding of the file format specification is required when using fpOdf; this complexity is hidden when using FPVectorial.
Forum Link:
Topic: fpOdf - Creating and modifying OpenDocument ODF files with freepascal
License
Modified LGPL (same as FPC RTL and Lazarus LCL).
Download
fpvectorial comes in the Lazarus SVN, in the directory components/fpvectorial:
svn co http://svn.freepascal.org/svn/lazarus/trunk/components/fpvectorial fpvectorial
See also fpvectorial
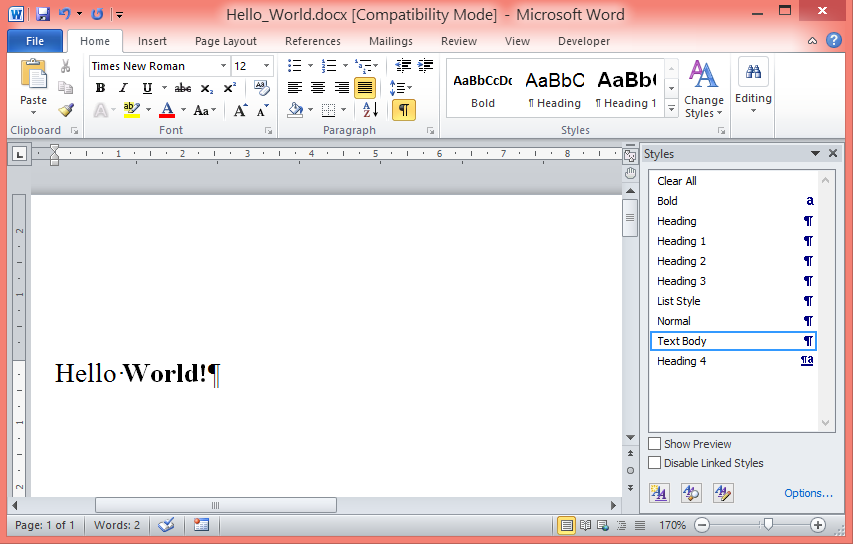
Hello World Example
The following code will produce a "Hello World" document. As no styles are defined, it is entirely up to the program used to open the resulting files (Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Write etc) to determine font and font size...
Program HelloWorld;
{$mode objfpc}{$H+}
Uses
fpvectorialpkg, fpvectorial;
Var
Document: TvVectorialDocument;
Page: TvTextPageSequence;
Paragraph: TvParagraph;
Begin
Document := TvVectorialDocument.Create;
Try
Page := Document.AddTextPageSequence;
Paragraph := Page.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.AddText('Hello World!');
Document.WriteToFile('Hello_World.docx', vfDOCX);
Document.WriteToFile('Hello_World.odt', vfODT);
Finally
Document.Free;
End;
End.
Basic Concepts
General
- A single FPVectorial Document (TvVectorialDocument) consists of a series of Page Sequences.
- Each Page Sequence can have it's own Header and Footer, and it's own Page Setup (size, orientation)
- Text, Tables, Images are added to the Page Sequence. In this way the document is built up.
- FPVectorial has no concept of how many pages are in a document, only the number of Page Sequences. A large multipage document may only have a single Page Sequence.
- A single Page Sequence can have multiple Paragraphs added.
- Headers and Footers are built up in an identical manner to a Page Sequence.
- TvVectorialDocument is responsible for freeing any entity added using the .AddXXX calls.
Formatted Text
- Text is added inside Paragraphs (TvParagraph).
- Paragraphs consist of multiple text runs or document fields. A single Paragraph can have a single Paragraph Style. Each text run can have an optional Text Style applied (allowing, for instance, the bolding of individual words in a paragraph).
- All Paragraph and Text Styles must be defined before being used.
- FP Vectorial supports style inheritance.
- Microsoft Office, OpenOffice and LibreOffice allow only partial styles to be defined, though each office implements its own different set of defaults for any missing properties. If it is critical that the document look identical in each of the Office Suites, then the Styles should be fully defined.
- A default set of Styles can be added to the FP Vectorial Document by calling AddStandardTextDocumentStyles.
- Headings are Paragraph Styles, with additional properties covering Heading Level and numbering
Document Fields
- Document Fields are added as TvField to Paragraphs via .AddField(AKind : TvFieldKind) : TvField
- Currently 5 simple fields are supported: vfkNumPages, vfkPage, vfkAuthor, vfkDateCreated, vfkDate
- fpvectorial holds no concept of current page or page count (only Page Sequences, which are separated by Section Breaks). Best guess values will therefore be added to the document during creation. The values can be updated in Microsoft Word by Selecting All, then pressing F9 (update fields). LibreWriter appears to automatically update the fields to correct values when opening the document.
- Numeric Fields can be formatted via TvField.NumberFormat as Decimal, lowercase/uppercase Roman or lowercase/uppercase Alphabetic
- Date Fields can be formatted cia TvField.DataFormat. Default value is 'd/MM/yyyy h:mm am/pm'
Tables
- Tables are centered around TvTable
- A TvTable consists of a collection of rows.
- Table rows consist of a collection of cells.
- Tables can add optional column information. This must be provided if merged cells are being used.
- Any Table Cell can support any document object, including multiple paragraphs, images and even nested Tables.
Lists
- Lists are centered around TvList.
- Each TvList can either have a TvParagraph added, or a child TvList (which is how we get deeper levels).
- Each TvList has both a TvStyle (which determines the default TvParagraph text appearance) and a TvListStyle (which determines the list behaviour).
- Each TvListStyle holds a list of TvListLevelStyle.
- Each TvListLevelStyle defines how each different level of the list behaves.
- Each List can be bulleted, or numbered.
- Supported numbering: Decimal, lowercase Roman, uppercase Roman, lowercase Alphabet, uppercase Alphabet.
- When dealing with numbered lists: Lists can be prefixed with single identifier (ie 1.) or numeric identifiers for all levels to date (ie 1.1.1.1.). This is handled through a boolean TvListLevelStyle.DisplayLevels.
- Two list styles are predefined in AddStandardFormats. StyleBulletList and StyleNumberList. Interestingly, the design for both docx and odt file formats (and consequently for fpvectorial) allow for a mixing of different list definitions within a list. So you can create a list that uses a mixture of the predefined StyleBulletList and StyleNumberList.
Roadmap
| Functionality | OpenDocument (ODT) | Office Open XML (DOCX) |
|---|---|---|
| File Version | ODT 1.2 with extensions | ECMA-376 1st Edition (2006) |
| Supported Style Types | Paragraph and Text-Span | Paragraph and Text |
| Table Support | Yes | Yes |
| List Support | Yes | Yes |
| Multiple Headers/Footers | Not yet | Yes |
| Tables in Header/Footer | Not yet | Not tested |
| Image Support | Not yet | Not yet |
| Images in Header/Footer | Not yet | Not yet |
| FPVectorial Image Support | Not yet | Not yet |
| Tab Stops | Not yet | Not yet |
| Document Fields | Yes | Yes |
| Meta Data | Partially Implemented | Not yet |
| Table of contents | Not planned | Not planned |
| Footnotes | Not planned | Not planned |
| Review/Revision | Not planned | Not planned |
| Bookmarks / Hyperlinks | Not planned | Not planned |
| Comments | Not planned | Not planned |
| Formulas | Not planned | Not planned |
Code Examples
Styles
This example uses both the default styles that can be added to TvVectorialDocument via AddStandardTextDocumentStyles, and a Text-Span style added specifically to TvVectorialDocument. Text-Span styles should not be applied to Paragraphs, only to individual Text Spans within a Paragraph.
Uses
fpvectorialpkg, fpvectorial;
Var
Document: TvVectorialDocument;
Page: TvTextPageSequence;
Paragraph: TvParagraph;
BoldTextStyle: TvStyle;
Begin
Document := TvVectorialDocument.Create;
Try
// Adds the defaut Paragraph Styles
// StyleTextBody, StyleHeading1,
// StyleHeading2 & StyleHeading3
Document.AddStandardTextDocumentStyles(vfUnknown);
// Add our own Style
BoldTextStyle := Document.AddStyle();
BoldTextStyle.Kind := vskTextSpan;
BoldTextStyle.Name := 'Bold';
BoldTextStyle.Font.Bold := True;
BoldTextStyle.SetElements := BoldTextStyle.SetElements + [spbfFontBold];
// Create the Document
Page := Document.AddTextPageSequence;
Paragraph := Page.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := Document.StyleTextBody;
// Add Hello World as two text spans within the same paragraph,
// and make 'World' bold
Paragraph.AddText('Hello ');
Paragraph.AddText('World!').Style := BoldTextStyle;
Document.WriteToFile('Hello_World.docx', vfDOCX);
Document.WriteToFile('Hello_World.odt', vfODT);
Finally
Document.Free;
End;
End.
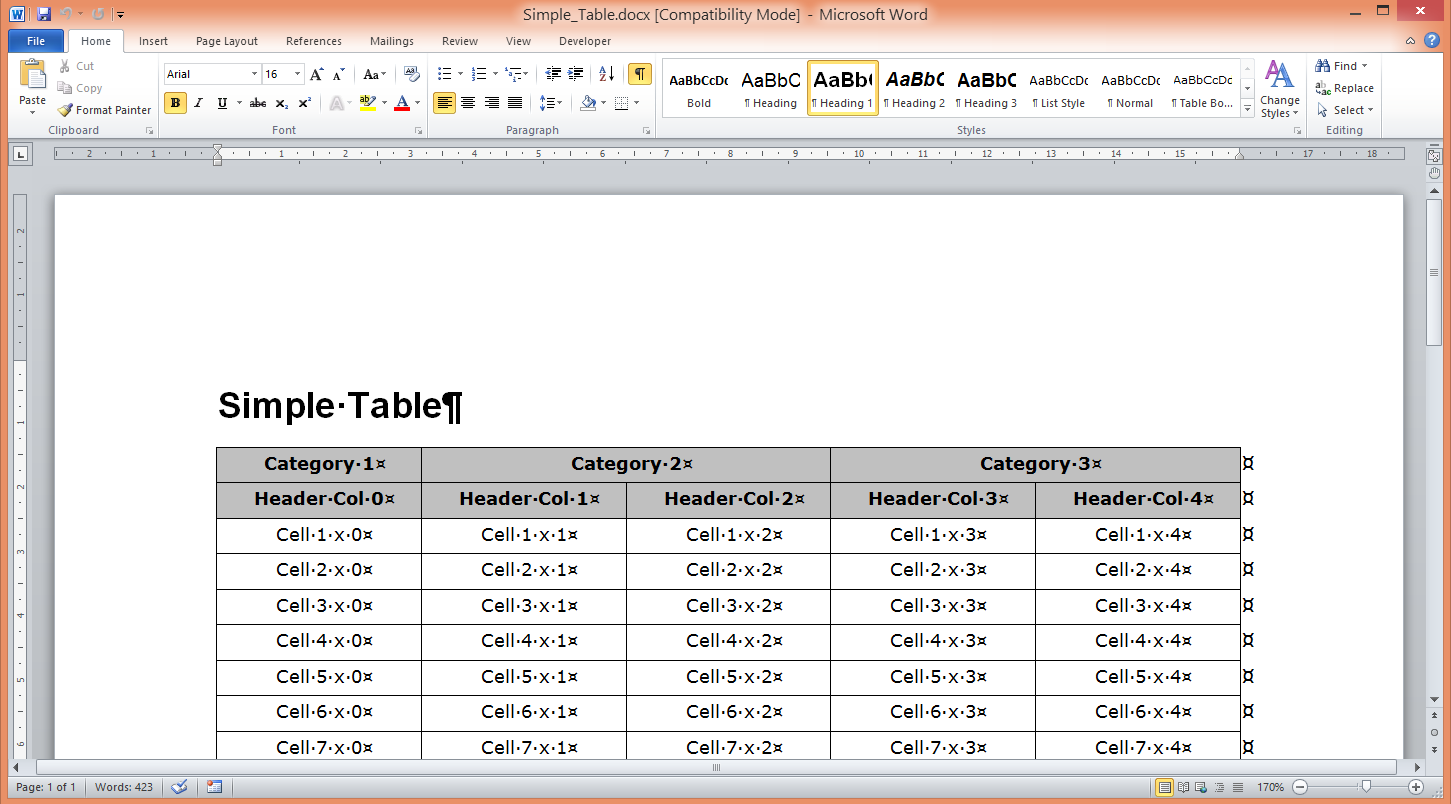
Simple Table
This example adds a 5 column table to the Document. The first two rows are designated as Header Rows (rows which repeat at the top of each page). These header rows then have a grey background shading applied, and the text is bolded.
The very first row contains examples of merging cells. Only 3 cells are added, with the last two cells spanning two columns each (set via .SpannedCols).
program SimpleTable;
{$mode objfpc}{$H+}
uses
fpvectorialpkg,
fpvectorial,
fpvutils, // For RGBToFPColor()
SysUtils;
var
Document: TvVectorialDocument;
Page: TvTextPageSequence;
Paragraph: TvParagraph;
BoldTextStyle: TvStyle;
CenterStyle: TvStyle;
Table: TvTable;
Row: TvTableRow;
Cell: TvTableCell;
iRow: Integer;
iCol: Integer;
const
// Most dimensions in FPVectorial are in mm. If you want to specify
// anything in other units, be ready to do the conversion...
ONE_POINT_IN_MM = 0.35278;
begin
Document := TvVectorialDocument.Create;
try
// Adds the defaut Paragraph Styles
// StyleTextBody, StyleHeading1,
// StyleHeading2 & StyleHeading3
Document.AddStandardTextDocumentStyles(vfUnknown);
// Add our own Style for bolded text elements
BoldTextStyle := Document.AddStyle();
BoldTextStyle.Kind := vskTextSpan; // This style will only be applied to selected Text Spans
BoldTextStyle.Name := 'Bold';
BoldTextStyle.Font.Bold := True;
BoldTextStyle.SetElements := BoldTextStyle.SetElements + [spbfFontBold];
// Add our own style for centered paragraphs
CenterStyle := Document.AddStyle();
CenterStyle.Kind := vskTextBody; // This style will be applied to the whole Paragraph
CenterStyle.Name := 'Table Body Centered';
CenterStyle.Font.Name := 'Verdana';
CenterStyle.Font.Size := 8;
CenterStyle.Alignment := vsaCenter;
CenterStyle.MarginTop := 2 * ONE_POINT_IN_MM;
CenterStyle.MarginBottom := 2 * ONE_POINT_IN_MM;
CenterStyle.SetElements :=
[spbfFontSize, spbfFontName, spbfAlignment, sseMarginTop, sseMarginBottom];
// Create the Document, and add a simple Heading
Page := Document.AddTextPageSequence;
Paragraph := Page.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := Document.StyleHeading1;
Paragraph.AddText('Simple Table');
// Add our Table, which will have 5 columns
Table := Page.AddTable;
Table.PreferredWidth := Dimension(100, dimPercent);
// As we will be merging cells, we have to define all the column widths
// so that ODT knows how many columns there will be.
// Getting the width exactly correct is not essential as LibreOffice Writer
// and Microsoft Word each treat this as a PreferredWidth value.
Table.ColWidthsUnits:=dimMillimeter;
Table.AddColWidth(50);
Table.AddColWidth(50);
Table.AddColWidth(50);
Table.AddColWidth(50);
Table.AddColWidth(50);
// Add a single row at the start which will contain merged cells
Row := Table.AddRow;
Row.BackgroundColor := RGBToFPColor(192, 192, 192); // Grey Shading
Row.Header := True; // Tell the table this is a Header Row
// Header Rows repeat at the top of each page
Cell := Row.AddCell;
Paragraph := Cell.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := CenterStyle;
Paragraph.AddText('Category 1').Style := BoldTextStyle;
Cell := Row.AddCell;
Cell.SpannedCols:=2; // Make this cell cover two columns
Paragraph := Cell.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := CenterStyle;
Paragraph.AddText('Category 2').Style := BoldTextStyle;
Cell := Row.AddCell;
Cell.SpannedCols:=2; // Make this cell cover two columns
Paragraph := Cell.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := CenterStyle;
Paragraph.AddText('Category 3').Style := BoldTextStyle;
// Add 21 rows to the Table, with the first being the header row
for iRow := 0 to 20 do
begin
Row := Table.AddRow;
// Header Row
if iRow = 0 then
begin
Row.BackgroundColor := RGBToFPColor(192, 192, 192); // Grey Shading
Row.Header := True; // Tell the table this is a Header Row
// Header Rows repeat at the top of each page
end;
// Add 5 cells to each Row
for iCol := 0 to 4 do
begin
Cell := Row.AddCell;
// Each Cell is a TvRichText, we cad add anything we can add to the main
// body of a Document (for now Paragraphs, Tables or Lists)
Paragraph := Cell.AddParagraph;
Paragraph.Style := CenterStyle;
if iRow = 0 then
Paragraph.AddText(Format('Header Col %d', [iCol])).Style := BoldTextStyle
else
Paragraph.AddText(Format('Cell %d x %d', [iRow, iCol]));
end;
end;
Document.WriteToFile('Simple_Table.docx', vfDOCX);
Document.WriteToFile('Simple_Table.odt', vfODT);
finally
Document.Free;
end;
end.
Lists
Sample code to create a List Style
Var
lCurListStyle : TvListStyle;
lCurListLevelStyle : TvListLevelStyle;
Begin
lCurListStyle := {TvVectorialDocument.}AddListStyle();
lCurListStyle.Name := 'Numbered List Style';
StyleNumberList := lCurListStyle;
for i := 0 To NUM_MAX_LISTSTYLES-1 Do
begin
lCurListLevelStyle := StyleNumberList.AddListLevelStyle;
lCurListLevelStyle.Kind := vlskNumeric; // Other option in vlskBullet
lCurListLevelStyle.NumberFormat:= vnfDecimal; // Other options include: vnfDecimal, vnfLowerLetter,
// vnfLowerRoman, vnfUpperLetter & vnfUpperRoman
lCurListLevelStyle.Level := i;
lCurListLevelStyle.Prefix := '';
lCurListLevelStyle.Suffix := '.';
lCurListLevelStyle.DisplayLevels := True; // 1.1.1.1.
//lCurListLevelStyle.DisplayLevels := False; // 1.
lCurListLevelStyle.LeaderFontName := 'Arial';
// Bullet is positioned at MarginLeft - HangingIndent
lCurListLevelStyle.MarginLeft := 16.35*(i + 1);
lCurListLevelStyle.HangingIndent := 6.35 + 3*i;
end;
end;
Sample code to create a List which includes entries at different levels of indentation.
Var
List : TvList;
SubList: TvList;
Begin
//...
// Missing code can be copied from above examples, this is a code snippet to demonstrate lists only
//...
// Add a simple heading
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleHeading2;
CurText := CurParagraph.AddText('Testing Lists');
// Indented numbered List
List := Page.AddList();
List.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
List.ListStyle := Vec.StyleNumberList;
// Start the list
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 1');
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 2');
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 3');
// The next three entries are are placed at Level 2
SubList := List.AddList;
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 1');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 2');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 3');
// The next three entries are are placed at Level 3
With SubList.AddList Do
begin
AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 1');
AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 2');
AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 3');
end;
// The next three entries are placed at Level 2
// NOTE: We are creating this SubList from the original List
SubList := List.AddList;
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 1 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 2 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 2, Item 3 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
// The next three entries are are placed at Level 3
SubList := SubList.AddList;
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 1');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 2');
SubList.AddParagraph('Level 3, Item 3');
// Three more entries in the original list
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 1 (Continuing on from same upper list)');
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 2 (Continuing on from same upper list)');
List.AddParagraph('Level 1, Item 3 (Continuing on from same upper list)');
// Mixing the original list with a sublist that utilises a different ListStyle
// In this case, bullets
SubList := List.AddList;
SubList.ListStyle := Vec.StyleBulletList;
SubList.AddParagraph('Bullet Level 2, Item 1 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
SubList.AddParagraph('Bullet Level 2, Item 2 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
SubList.AddParagraph('Bullet Level 2, Item 3 (new SubList added to same upper List)');
Conceptual Output from the above code:
- 1. Level 1, Item 1
- 2. Level 1, Item 2
- 3. Level 1, Item 3
- 3.1. Level 2, Item 1
- 3.2. Level 2, Item 2
- 3.3. Level 2, Item 3
- 3.3.1. Level 3, Item 1
- 3.3.2. Level 3, Item 2
- 3.3.3. Level 3, Item 3
- 3.4. Level 2, Item 1 (new SubList added to same upper List)
- 3.5. Level 2, Item 2 (new SubList added to same upper List)
- 3.6. Level 2, Item 3 (new SubList added to same upper List)
- 3.6.1. Level 3, Item 1
- 3.6.2. Level 3, Item 2
- 3.6.3. Level 3, Item 3
- 4. Level 1, Item 1 (Continuing on from same upper list)
- 5. Level 1, Item 2 (Continuing on from same upper list)
- 6. Level 1, Item 3 (Continuing on from same upper list)
- • Bullet Level 2, Item 1 (new SubList added to same upper List)
- • Bullet Level 2, Item 2 (new SubList added to same upper List)
- • Bullet Level 2, Item 3 (new SubList added to same upper List)
Document Fields
The following code snippet shows how Document Fields are added:
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
CurParagraph.AddText('Page Count: ');
CurParagraph.AddField(vfkNumPages);
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
CurParagraph.AddText('Page: ');
CurParagraph.AddField(vfkPage);
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
CurParagraph.AddText('Author: ');
CurParagraph.AddField(vfkAuthor);
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
CurParagraph.AddText('Date Created: ');
CurParagraph.AddField(vfkDateCreated);
CurParagraph := Page.AddParagraph();
CurParagraph.Style := Vec.StyleTextBody;
CurParagraph.AddText('Date: ');
CurParagraph.AddField(vfkDate);
Output from above:
- Page Count: 3
- Page: 2
- Author: FPVECTORIAL
- Date Created: 24/09/2013
- Date: 24/09/2013 2:08 PM
Known Issues
- Table support in ODT writer results in large file sizes. This is due to the fact that a style is created for each individual cell, even if multiple cells are identically formatted. This also applied to row styles and column styles. In order to resolve this, Cell, Row and Column Styles could be normalised. Alternatively, the entire table formatting architecture could be re-written to force the end user to create and apply the styles themselves (in addition to also requiring DOCX table support to be re-written to support the new architecture, specific code will need adding to DOCX writer to interpret the new FP Vectorial Table Styles).
- ODT Writer produces files that cannot be opened in Word 2010.
- File MIMETYPE in ODTDocument should not be compressed. Currently clNone compression type is ignored by TZipper (possible cause for Word 2010 rejecting existing ODT files). Patch exists, but not yet added to FPC Trunk (See http://mantis.freepascal.org/view.php?id=24897 & http://mantis.freepascal.org/view.php?id=23533).
- Double line not supported in ODT Tables. Two locations in ODTVectorialWriter.pas need to changed to enable support:
- LU_BORDERTYPE needs double adding (in CONST at start of unit. currently double is mapped to solid)
- function TvODTVectorialWriter.BordersToString needs to support double (see comment at start of function)
TODO
General
- Comprehensive testing, including opening the files in as many word processors and office suites as possible.
- DOCX and ODT Readers (volunteers required)
- Add PDF reader/writer (current PDF support is for Vector Image support only)
- Add HTML reader/writer
- Add RTF reader/writer
- Produce well documented examples and store in FPVectorial/Examples
- Code Documentation for distributing with Lazarus
New Code
See Roadmap above...
ODTWriter
- Support for Header/Footers and support for Tables within Headers/Footers. This requires a refactoring of ODT writer. Header and Footer content is actually stored in styles.xml, not in content.xml. All current text and table support can only produce content in content.xml.